
Popular Online Analytical Analytical Processing (OLAP) server technologies such as Pentaho Mondrian Project, JasperReports, and Microsoft SQL Server Analysis Services (SSAS) enable business users to analyze large quantities of data, offering features such as drilling into and cross-tabulating information from complex analytical queries in real-time. However, the default user interfaces (UIs) are limited, and it can be difficult or impossible to add the additional behaviors that are typically needed when integrating with a larger application. Connecting CubeGrid APIs to these multidimensional, or ‘cube’, data sources will allow you to:
The CubeGrid is a high-end data analysis engine that wraps OLAP functionality into a single Smart GWT or SmartClient interactive grid component for fast access to multidimensional data and calculations. Please see our previous blog post, Introducing the CubeGrid, for more information about the advanced OLAP features in our Analytics Module.
This article explains how to connect the CubeGrid user interface to several common sources of cube data using MDX, XMLA, and OLAP4J.
OLAP Server | Company | Version | Language | License |
Pentaho Mondrian Server | 3.4.0 | Java | ||
JasperReports Server | 4.5.0 | Java | ||
Microsoft SQL Server | 2012 | C++ |
Multidimensional data sets are called Data Cubes, which consist of features or attributes called Dimensions. Each corresponding Dimension will also have feature values or attribute values called Members. These definitions have analogous nomenclature in the CubeGrid, as shown in the table below:
OLAP | CubeGrid | Definition |
Data cube | Cube | Multidimensional dataset |
Dimension | Facet | Dimension, attribute, or feature |
Member | Facet value | Dimension member, attribute value, or feature value |
On the server side, we first need to set up our DataSources to fetch the necessary data. We have four Java Classes for our DataSources:
The selected Data Cube and Dimensions are sent from client to server as criteria obtained from DSRequest.
Lastly, the DBConnection Java Class is required for connection to the chosen OLAP server. There are three variations of the getConnection() method:
On the client side, we already have the code required to interface with the CubeGrid. This is very similar to the Advanced Cube sample in the Showcase, except that Data Cubes, Dimensions and associated Members are fetched dynamically.
The software versions used in this sample are:
Download the project source code used in the examples here.
Lastly, we’ll show a few images of the Project in action.
Figure 1: Creating the CubeGrid from a connected OLAP server (from left to right)

Figure 2: The newly created CubeGrid with Control Panel for Dimension (Facet) manipulation
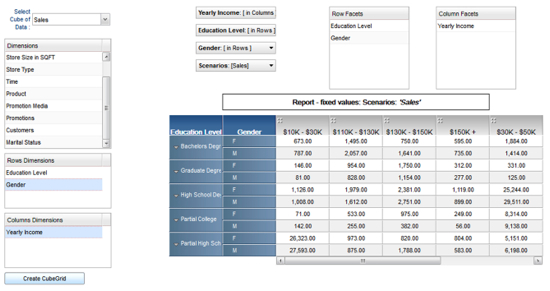
Figure 3: View Members (Facet Values) of selected Dimensions (Facets) using the Control Panel
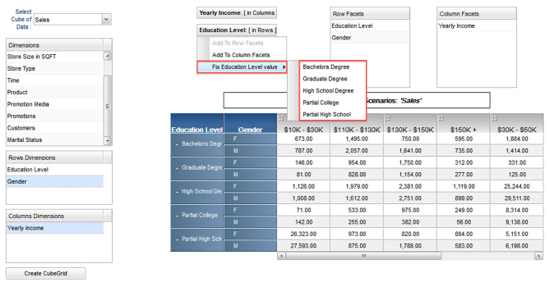
Figure 4: Reposition Dimensions (Facets) on the fly for alternate views

Note that the UI shown above is built out of ordinary Smart GWT components such as ListGrids and Menus (and of course the CubeGrid). This means that, unlike the pre-built UIs bundled with OLAP products, the UI shown above can be easily rearranged and extended. For example, you could add context menus that launch application-specific actions when the user right-clicks on data or dimension values.
Please Note: Some Dimensions in the test cubes are very large and not collapsible due to their non-hierarchical nature. For example, the ‘Customers’ dimension in the ‘Sales’ cube sample for Mondrian shows all values. As a result, the cube may become difficult to navigate or show a slow scripts browser warning. The recommended way to avoid this is to require that the end user choose specific members from large dimensions before adding them to the cube.